I have a modest financial investment in Insig AI.
This article highlights various financial companies that have incorporated AI technology in their operations or provide a range of AI products, investment data, and governance. It is a mad world of corporate finance where AI has been playing a part for much longer than you may be aware.
I also discuss AI, greenwashing and ESG, the latter of which is, as far as I am concerned, just another stealth tax crime against the general population; not to argue that we do not need to look after the planet; we do, not least because it is the only one, we have until Elon Musk has worked out how to get us to Mars. That said, I do not see myself thumbing a lift even if I had the funds in the unlikely event; jetting off to Belgium on a Ryan Air 737 is about as much excitement in the air as I can handle.
There is much discussion regarding AI and Environmental Social Governance (ESG), with some expressing fear about its potential impact for different reasons. Certain influential individuals have been critical of AI’s development and are calling for a “pause” in its progress until proper checks and balances are established to safeguard humanity. Skipping the political aspect of what people are saying about AI, and ESG for that matter, I will concentrate on Insig AI’s role, including looking a little deeper into a recent presentation the Company made at The City of London Club on “Generative AI and how we’re focused on being part of this seismic change!”
Before I do, it is worth referencing a Wall Street Journal article.
The article discusses PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) plans to invest $1bn in generative AI technology in its US operations over the next three years, working with Microsoft and OpenAI to automate aspects of its tax, audit and consulting services. The investment will include funding to recruit more AI workers and train existing staff in AI capabilities and potential acquisitions of AI software makers. PwC’s goal is to embed generative AI into its own technology stack and client-services platforms, as well as to advise other companies on how best to use the technology, said Mohamed Kande, PwC’s vice chair and co-leader of US consulting solutions and global advisory leader.
It should therefore be noted Insig AI has been chosen to participate in PwC’s Scale FinTech program, which provides access to new commercial opportunities within PwC and its clients. Insig AI was selected from a pool of over 700 applicants around the world and was one of only nine companies chosen for the programme this year. Insig AI is also the only FinTech with ESG expertise in the programme. PwC, in partnership with Growth Builders, has been running the Scale FinTech programme for five years, targeting technology scale-ups with innovative FinTech solutions.
Additionally, KPMG UK’s new Head of ESG, Richard Andrews, intends to integrate ESG throughout the business and ensure it becomes “the watermark that runs throughout the firm”. At present, KPMG UK’s clients are coming to the Company with a range of complex challenges related to their ESG agenda, including reporting, transition planning and decarbonisation programmes. Andrews said high-quality, internationally consistent ESG reporting standards are required to guarantee a successful reporting ecosystem. Mandatory reporting requirements, such as the Taskforce for Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) in the UK, significantly impact climate and broader ESG considerations in boardrooms. The firm is committed to implementing the necessary systems, processes, and controls to aid corporates with reporting. The new Head of ESG will be responsible for building and strengthening KPMG’s ESG capabilities, bolstering partnerships across the industry, and enhancing the Company’s technology to help its clients respond to the challenges and opportunities ESG presents.
Is AI new in finance?
No – AI may appear as a new technology because everyone is talking about AI chatbots and Elon Musk Neuralink, which is focused on developing brain-machine interfaces (BMI) that could allow humans to merge with AI. But city institutions have been using AI for decades to boost investment returns. However, the use of AI in finance has become more prevalent in recent years with the increasing availability of data and advances in computing power. Moreover, AI is being used by city institutions and Companies across all industries to monitor their ESG credentials.
One early example of the use of AI in finance is the development of automated trading systems in the 1980s. These systems used AI algorithms to analyse market data and make trading decisions. Over the years, AI has been used in various applications in finance, including fraud detection, credit scoring, and risk management.
Machine learning (ML) techniques such as deep learning and reinforcement learning have been applied to finance with promising results. For example, these techniques have been used to build predictive models for stock prices, identify market trends, and optimise investment portfolios. Two of the most prolific companies using ML/AI since their inception to trade and find alpha are Renaissance Technologies (Jim Simmons) and Bridgewater (Ray Dalio).
Renaissance’s flagship Medallion Fund generated 62% annualized returns (before fees) and 37% annualized returns (net of fees) from 1988-2021.
AI Companies of interest
Several private companies use AI data to improve fund manager performance and investment returns. However, I have no idea how any of the following examples compare to what Insig AI offers.
Kensho Technologies was acquired by S&P Global in 2021. The Company uses big data, machine learning, and natural language processing to provide investment research in national security industries, including recommendations to fund managers.
Ayasdi was acquired by Symphony AI Sensa in 2022. The Company leverages AI and machine learning to offer investment optimisation and risk management solutions to financial institutions and asset managers. Nevertheless, its primary area of expertise is analysing patients’ healthcare data to uncover novel insights into disease pathways, treatment options, and other crucial aspects.
Truvalue Labs is a technology company that provides innovative solutions for clients in the finance and sustainability industries. Truvalue Labs was acquired by Factset in 2020. Its primary product is an AI-based platform that uses natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to analyse unstructured data from various sources, including news articles, research reports, and social media. As a result, the platform can quickly identify and extract insights related to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors that can impact a company’s performance and long-term sustainability.
Truvalue Labs’ appears to be the closest match to what Insig AI does. Its platform has been widely adopted by clients in the finance industry, including asset managers, hedge funds, and other institutional investors. The platform’s real-time ESG insights can help clients make informed investment decisions, reduce risk, and improve long-term performance, therefore, an attractive acquisition.
BlackRock (BLK), the most notorious, is the world’s largest asset manager and uses AI and machine learning to analyse large amounts of data and make better investment decisions.
Goldman Sachs (GS) has been using AI in its trading operations for many years, and more recently, the firm has been investing heavily in AI and data science to improve its investment research and portfolio management.
JPMorgan Chase (JPM) has been using AI and machine learning to develop investment strategies and improve its trading operations.
Man Group (EMG.L) is a London-based hedge fund that uses AI and machine learning to analyse market data and make better investment decisions.
AQR Capital Management (AQR) – is a quantitative investment management firm using AI and machine learning to develop investment strategies and optimise portfolios.
I also had an exchange with Steven Cracknell, CPO of Insig AI. He was kind enough to explain the sector consolidation, investment and, importantly, Insig AI differentiator.
“Most of the Companies you mention are major global organisations that have invested (continue to invest) billions of USD into technology, data and AI. I would go further to add some other major players in the ESG data market, which are the rating agencies and financial market vendors:”
MSCI, S&P Global, Fitch, Bloomberg, Refintiv, Moody’s
“There is certainly an active data ‘land grab’ on the go with the consolidation of offerings quite commonplace, and interestingly, three of the Companies you identified have all been acquired by some of the big players recently.”
“Even being listed in the same breath as these companies are hugely flattering and complimentary. I wouldn’t say that Insig AI competes with any of these names directly, given their sheer size (and bank balance!).”
“In terms of the large AMs, they are in their own league and aim to rule the world. Hence, they are competing against every other asset manager.”
“So, whilst Insig AI cannot compete directly against them, it can help small to mid-size asset managers migrate over to using the latest AI and ML technology by unlocking their data and providing them access to advanced ML models and tools that would take them years to build (let alone hire a competent team to build it themselves).”
“So, the Insig AI differentiator is Implementation, Execution and Speed BUT for the direct benefit of its clients.”
“Insig AI clients get the benefit of being at the cutting edge without needing to hire an entire team of data engineers and data scientists.”
“In terms of our data collection and transformation capabilities (specifically ESG), again, our differentiator is speed and making data accessible to our clients, but in a format immediately useful to them.”
“The big data vendors may sell similar data sets but in ‘their’ format. This immediately places a burden on any asset managers who don’t have in-house technical skills to ingest and transform the data to suit their systems.”
What is “greenwashing”, and how does it sit within the ESG framework?
Greenwashing is a marketing tactic companies use to present themselves or their products as environmentally friendly, sustainable, or socially responsible, even though they may not be. This practice involves making misleading or false claims about a company’s environmental or social impact to improve its reputation or increase sales.
Greenwashing is related to ESG because ESG is a framework used by investors and companies to evaluate a company’s sustainability and ethical practices. ESG criteria assess a company’s environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices.
Where does Insig AI fit in?
Insig AI appears to have a unique set of tools which could play a significant role in monitoring and policing corporate accounts being greenwashed for ESG credentials, which could significantly impact financial institutions and fund managers. In recent years, ESG investing has become increasingly popular among investors who prioritise social responsibility and environmental sustainability in their investment decisions. However, there is growing concern that some Companies may exaggerate or misrepresent their ESG credentials, which could lead to financial institutions and fund managers unknowingly investing in Companies that do not meet ESG standards, which can have financial consequences.
Insig AI has partnered with CarVal Investors, LP, to integrate their ESG tools with CarVal’s ESG risk scoring methodology for the upcoming CarVal Clean CLO product line. This collaboration marks the first implementation of Insig’s and CarVal’s jointly developed ESG technology. With a deep understanding of fixed income, Insig AI empowers asset managers to create and implement a data-driven ESG investing strategy that is performance-oriented. It offers transparent and evidence-based ESG scoring and analysis, while also enabling comparison to relevant benchmarks.
Diana Rose, ESG research director at INSIG AI, explains, “The regulatory landscape in the investment and corporate world is changing. But unfortunately, some companies and fund managers may not be ready for the ESG pitfalls.”
“The regulatory landscape is changing fast. We believe Insig AI is in a powerful position to support financial institutions now and in the future, as regulation is set to keep tightening in the US, Europe and the UK.”
“There are two aspects to greenwashing as I see it – corporate and financial – the regulators are gaining traction in clamping down on both, and Insig’s AI offering is relevant to both.”
It is difficult to determine how many companies have fallen foul to misrepresenting their ESG credentials, knowing or falsifying their account, as it can vary depending on the jurisdiction, regulatory body, and timeframe.
For example, in the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has brought several enforcement actions against companies for misleading ESG claims.
Similarly, in the United Kingdom, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) has acted against several companies for greenwashing. For example, in 2021, the FCA fined Aviva Investors, a global asset manager, £17.6 million for misleading customers about the environmental impact of its investments. However, that was not the end of the penalty; The Company had previously paid compensation of £132 million directly into client funds as redress.
Other Examples:
- SEC, they issued a $1.5m fine to BNY Mellon Investment Adviser for misleading investors on their ESG funds.
Nestle and Coca-Cola have also faced scrutiny for their environmental practices and have been accused of greenwashing. While they have taken some steps to reduce their environmental impact, many argue that they must do more to address the larger issue of plastic pollution and climate change.
Volkswagen tops the greenwashing league table and has faced severe consequences for its involvement in the “Dieselgate” scandal. The Company had to pay billions in fines and settlements, including $14.7 billion to the US Environmental Protection Agency, Department of Justice, and Federal Trade Commission. This settlement compensated affected customers, funded environmental projects, and imposed penalties for violating the Clean Air Act. Additionally, Volkswagen paid $4.3 billion in a separate settlement with the US Department of Justice, which included criminal fines and penalties, and agreed to pay $1.2 billion to settle claims by US VW dealerships affected by the scandal. The Company also faced fines and penalties in Germany, France, and South Korea, resulting in an overall estimated payment of $30 billion in fines and settlements.
Recently, Vivek Ramaswamy wrote an article for the Wall Street Journal criticising ESG investing and suggesting that Silicon Valley Bank’s commitment to sustainable finance and carbon neutrality contributed to its collapse. However, the Financial Times disagreed with Ramaswamy’s argument; but they were equally wrong because they were both half right. SVB failed due to poor management and a lack of attention to market trends, such as rising interest rates. In addition, the bank’s risk manager was off on a jolly for nine months planning a pride event; no, I am not joking.
Integrating ChatGPT and GPT4…
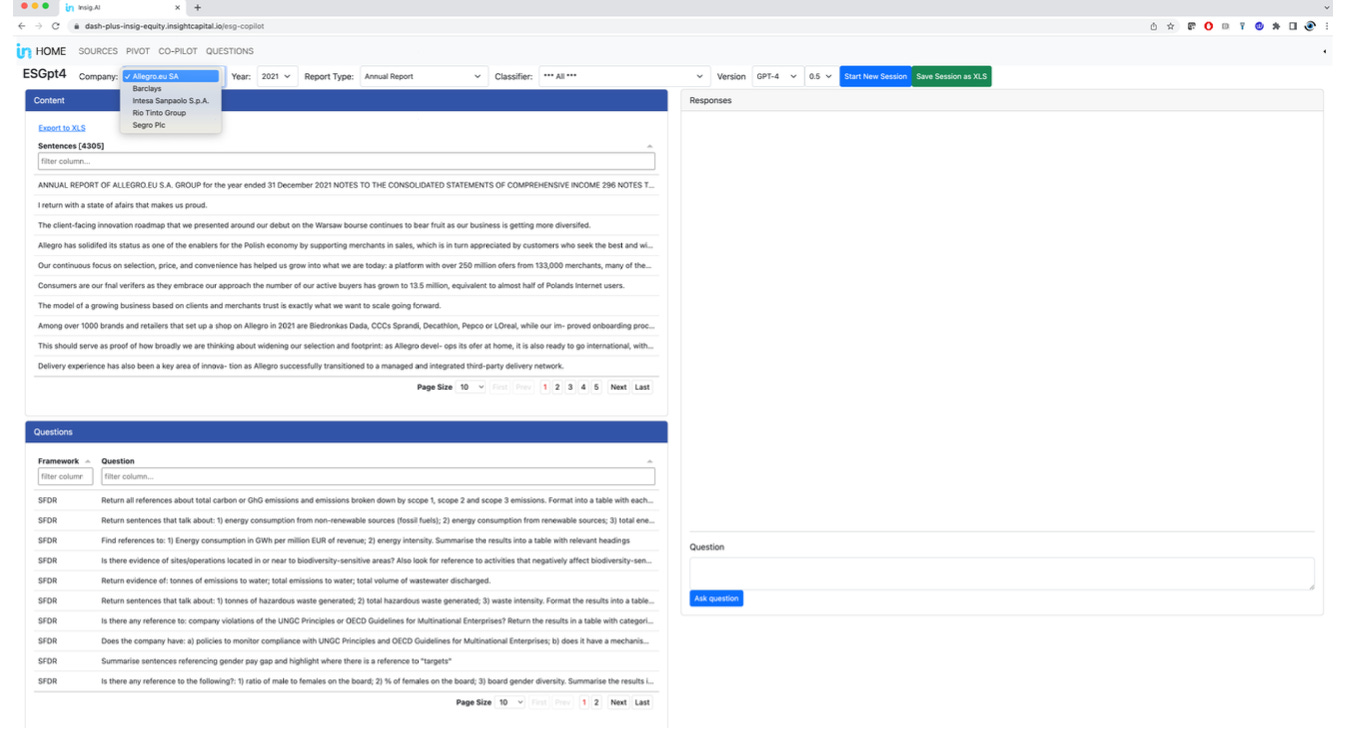
Insig AI says it can integrate AI capabilities from Google, Open AI, ChatGPT and GPT-3 and ChatGPT-4 into its ESG Research Tool and the NLP classifier, which can help financial institutions and fund managers identify potential instances of greenwashing in corporate accounts. For example, the NLP classifier can score text against 15 E, S, and G issues, providing metadata tags like GICS classification and document classification. As a result, financial institutions and fund managers can better understand a company’s ESG performance and determine if it meets its investment criteria by analysing this data. Additionally, Insig AI’s ability to provide original PDF and machine-readable text and facilitate the collection and tagging of different companies can result in a shared valuable dataset for data-driven insights.
The importance of monitoring and policing of corporate accounts for greenwashing is crucial for financial institutions and fund managers who want to ensure that they are investing in companies that meet ESG standards. Failing to do so could lead to reputational damage, loss of investors, and even legal repercussions. By using Insig AI’s tools, financial institutions and fund managers can make more informed investment decisions and avoid investing in companies that do not meet their ESG standards.
Furthermore, using Insig AI’s tools could have a broader impact on the financial industry’s approach to ESG investing. By encouraging greater transparency and accountability among companies, financial institutions and fund managers can incentivise companies to improve their ESG performance and reduce the risk of greenwashing. This, in turn, could lead to a more sustainable and responsible financial system, benefiting investors, society, and the environment.
FCA TechSprint 2023 Targeting Greenwashing
• 13 international regulators
• Tackle or mitigate the risks of greenwashing in financial services across the globe
• Use AI and Machine Learning to verify that ESG-related product claims are accurate and complete
The FCA TechSprint 2023 Targeting Greenwashing is a concerted effort by international regulators to tackle the problem of greenwashing, or companies making false or misleading claims about their environmental credentials, in financial services. Insig AI and Machine Learning will help verify the accuracy and completeness of ESG-related product claims made by financial services firms, enabling regulators to identify any instances of greenwashing.
By using technology to monitor, collate and identify examples of greenwashing from financial services firms’ websites, social media platforms and other documentation or data, regulators can better understand what is being claimed and how these claims are being made. This can lead to more effective oversight and a more robust approach to policing greenwashing, enabling regulators to share information and best practices across different jurisdictions. Ultimately, this will increase transparency and promote greater accountability in financial services, helping to ensure that companies are held to account for their environmental credentials and their impact on the planet.
The FCA collaboration is expected to attract a mix of grudge and discretionary buys of the Insig services.
Generative AI: Why Integrate?
1. Because we can
2. We have our own data
• Corporate and ESG filings from 2015
• 4,000 companies
• 160,000 unique reports
• 110,000,000 machine-readable sentences
3. We have the infrastructure to scale
• High volume data ingestion and transformation pipeline
• High-speed NLP scoring framework
• Elastic search as a service
The above information highlights the benefits of integrating generative AI, which can help with data transformation and scoring. Additionally, the Company’s data details, including corporate and ESG filings, machine-readable sentences, indicate significant data that can be harnessed for predictive analytics and other data-driven insights. The information on the Company’s infrastructure to scale, including high volume data ingestion and transformation pipeline, high-speed NLP scoring framework, and elastic search-as-a-service, suggests that the Insig AI can handle and manage its data effectively and efficiently. Therefore, understanding this information could be helpful in corporate account management tasks, hence the Company’s collaboration with the FCA and its role in the Global Financial Innovation Network’s (GFIN) Greenwashing TechSprint, to be launched on 5 June 2023. Additionally, because companies publish all throughout the year, data collection and updates are continuous.
To give you a practical example of this, since the presentation on 27 April 2023, illustrated above, we have continued to update our company database:
Numbers as of 5 May 2023
• 4,139 companies
• 175,485 unique reports
• 114,692,418 machine-readable sentences
Chief Product Officer & Co Founder, Steven Cracknell: “explains, that although they don’t directly compete with the large data vendors, their infrastructure and data collection costs are significantly lower. Their ability to easily adjust processing speed and power gives them a competitive advantage. As a small and well-engineered AI company, they prioritise efficiency and use their own tools to benefit their clients.”
Insig AI can contribute to the FCA Tech Sprint by using the following steps:
- ESG Research Tool: Insig.AI can use its ESG Research Tool to access all the data within the database.
- Document level scores and metadata tags: They can use their NLP classifier to identify and score text against 15 E, S, and G issues. They can also add metadata tags like GICS classification, document classification (report group, type, and title), date, entity identifiers, and region/index.
- Data download: Insig.AI can provide the original PDF and machine-readable text for Rio Tinto’s 2021 annual report.
- Document upload and tagging: They can facilitate the collection and tagging of other companies into the shared dataset for Tech Sprint participants.
- Workshops to assist with data analysis: In these workshops, Insig.AI can teach participants how to combine NLP classifiers and keywords to surface disclosure patterns and how to apply ChatGPT to ESG disclosure data.
Insig AI can use the above steps to help FCA Tech Sprint participants better analyse and understand ESG data. The outlined steps are critical in supporting the FCA Tech Sprint 2023 Targeting Greenwashing. Using Insig’s ESG Research Tool can allow easy access to pertinent data. At the same time, the NLP classifier can provide a score for text against 15 E, S, and G issues, along with metadata tags like GICS classification and document classification.
Insig AI can also offer workshops to train participants on combining NLP classifiers and keywords for effective disclosure pattern identification and utilising ChatGPT for ESG disclosure data. These steps can aid in creating a more robust approach to preventing greenwashing and promoting transparency and accountability in financial services, ultimately contributing towards environmental protection.
Business Model
So how is Insig AI to build revenues from its technology suite? Insig AI has announced that it expects to generate significant and long-term revenues after the commercialisation of AB CarVal’s ESG Scoring Tools. The company has highlighted the importance of ESG risk assurance in the corporate audit process and emphasised that it is in a strong position to provide this through strategic partnerships. In addition, the company has identified a revenue stream by assisting asset managers in improving investment returns and reducing financial risk. Insig AI has expressed concern about the number of asset managers that still rely on outdated systems, which highlights the potential for growth in this market.
Non-Executive Chairman Richard Bernstein commented, “Our collaboration with the FCA centres around our ESG rationale: preventing and policing corporate wrongdoing. Big business and the asset management industry have a responsibility to behave as good corporate citizens. We have a massive database of evidence should they fall short.”
In conclusion, Insig AI’s unique tools have the potential to play a critical role in monitoring and policing corporate accounts for greenwashing in ESG investing. As a result, financial institutions and fund managers should consider leveraging these tools to make more informed investment decisions, avoid investing in companies that do not meet their ESG standards, and encourage greater transparency and accountability among companies. Ultimately, this could lead to a more sustainable and responsible financial system that benefits all stakeholders.
Investors have experienced some difficulties since the RTO, but there are indications that not only is the Company is making progress in gaining commercial traction with AB CarVal, the FCA looks to be an outstanding opportunity. The next 12-18 months will be crucial in demonstrating a fully funded, profitable transition that will significantly increase the value of the shares. In the meantime, last month, the Company announced an equity funding with a new institutional investor and a forecast that no further funding should be required before profitability. Adding further comfort is Chairman Richard Bernstein’s decision to become an Executive director, his £150,000 investment as part of the fundraiser and his recent share purchase in the after-market. Insig AI has positioned itself ideally at the forefront of data science, machine learning, generative AI and collaborating with 14 international regulators to combat greenwashing.
If you have not already watched it, a demonstration video by CEO Steve Cracknell is worth watching.
Elric Langton of Small Company Champion & Lemming Investor Research Newsletter
Twitter: @LEMMINGINVESTOR
Got some thoughts on this week’s article from Elric? Share these in the SharePad chat. Login to SharePad – click on the chat icon in the top right – select or search for a specific share.
This article is for educational purposes only. It is not a recommendation to buy or sell shares or other investments. Do your own research before buying or selling any investment or seek professional financial advice.